Android development is one of the most lucrative fields of software development. Currently, 75.16% of all mobile users worldwide use an Android device. It’s also very likely that Google’s Android operating system will continue retaining its market position in the future as well.
Thanks to Google and third-party developers, Android has an incredibly huge ecosystem and an active community. In this collection, you can find 12 key tools and resources you need to know if you want to build professional mobile applications on the Android platform.
1. Android Studio
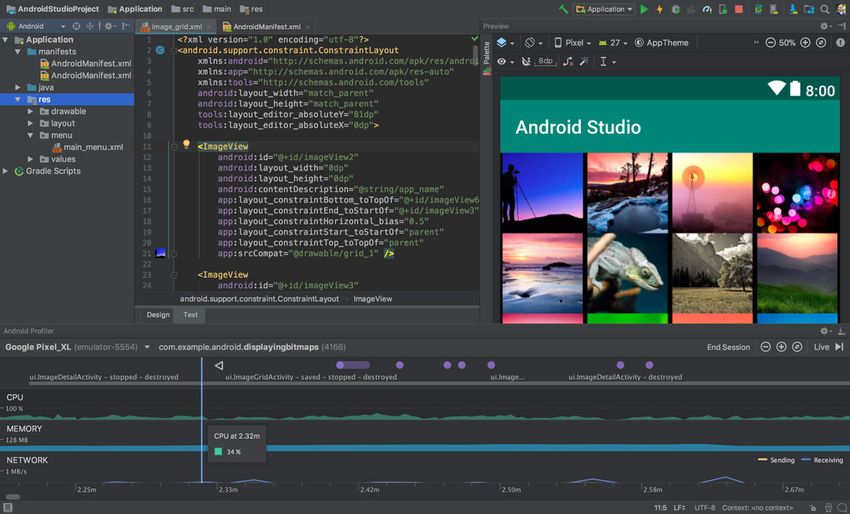
Android Studio is the official IDE (Integrated Development Environment) for Android development, created by Google. You can use it to build Android apps on Windows, Linux, and macOs operating systems. Android Studio supports all programming languages you can use for Android development: Java, C/C++, and Kotlin.
It comes bundled with Android SDK (Software Development Kit) and some additional development tools such as AVD Manager and Android Debug Bridge. Android Studio includes a visual layout editor, an APK (Android Package) analyzer, an Android device emulator, and real-time performance profiling tools, too.
2. AVD Manager
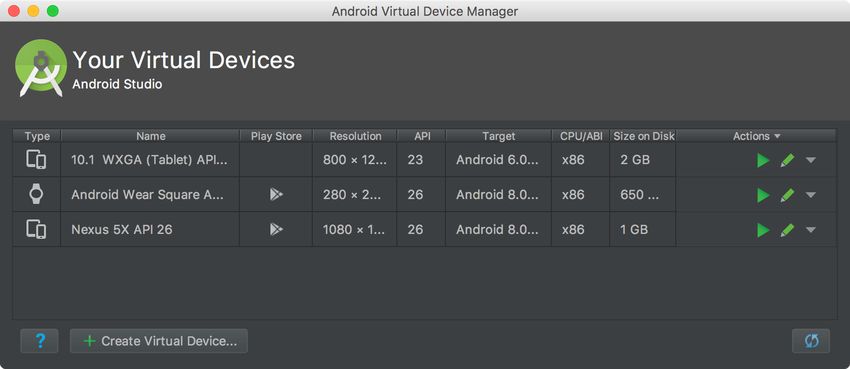
AVD Manager is a built-in tool of Android Studio. AVD stands for Android Virtual Device. It makes it possible to create virtual Android devices for testing purposes. An AVD is a configuration that describes the characteristics of a virtual device such as hardware profile, storage area, appearance, system image, and other attributes.
With AVD Manager, you can create as many AVDs as you want. You can access your virtual devices for testing purposes in the Android Emulator that also comes bundled with Android Studio.
3. Android Jetpack
Android Jetpack is a collection of Android components and tools created by Google. You can use them for managing typical Android development tasks. Jetpack components are grouped into four categories:
- Foundation: backward compatibility, testing, Kotlin support, etc.
- Architecture: data binding, lifecycles, navigation, etc.
- Behavior: notifications, preferences, sharing, etc.
- UI: animations, layout, emojis, etc.
Jetpack components are bundled as androidx.* package libraries. You can find all Jetpack components in the AndroidX Package Index. AndroidX ships separately from Android OS in order to provide backward compatibility across different Android releases.
4. IntelliJ Idea

IntelliJ IDEA is a Java IDE with built-in Android support, created by JetBrains. Although Android Studio is the official Android IDE, IntelliJ IDEA is also an excellent choice for simpler Android applications. Especially, since Android Studio itself is built on top of IntelliJ IDEA. You can find a detailed Android development guide in IntelliJ IDEA’s documentation.
With IntelliJ IDEA, you get access to features like clever code completion, on-the-fly code analysis, refactoring tools, and a lot of useful JetBrains plugins. If you’re interested in how it compares to Android Studio, have a look at Slant’s IntelliJ IDEA vs Android Studio comparison. IntelliJ IDEA has both Community and Ultimate (commercial) Editions.
5. AIDE
AIDE stands for Android IDE and it allows you to build Android applications right on your Android phone or tablet. It provides a very convenient way for Android development. You can’t only write the code on your device but also run, test, and debug the app in the same environment. You can download AIDE from the Google Play store.
Although AIDE doesn’t have as many features as other IDEs such as Android Studio and IntelliJ IDEA, it’s a great solution for less experienced programmers. It includes Android tutorials that let you follow highlighted code and run the example app right on your device. AIDE currently supports Android apps written in Java and C/C++. So, if you want to build apps in Kotlin, you need to choose another Android IDE.
6. B4A
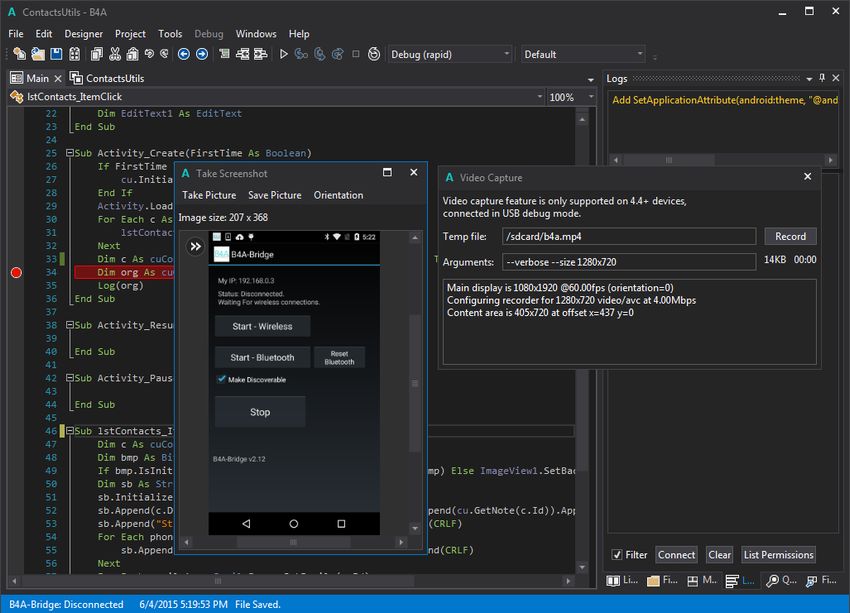
B4A (Basic for Android) is an Android IDE that allows you to develop Android apps using the BASIC programming language. Although BASIC is not the typical choice for Android development, it’s much easier to get started with. BASIC was designed with beginners in mind, so it’s close to the regular English language.
B4A comes with many user-friendly features such as a visual editor, a step-by-step debugger, and a UI cloud service with which you can test your app on a cloud of real-world devices. B4A is not free (see pricing) but it offers a 30-day free trial, plus a 30-day money back guarantee for the Full version.
7. Unity 3D
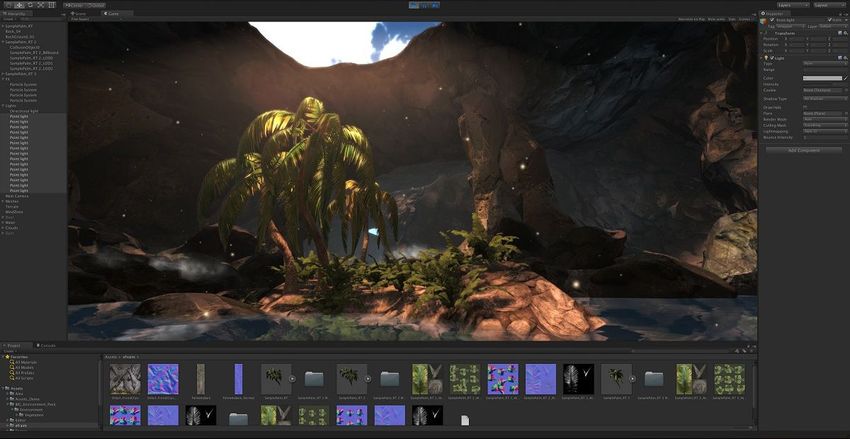
Unity 3D is a cross-platform game engine and IDE you can use for creating graphic-intensive mobile games. Although you can also build Android games with Android Studio and IntelliJ IDEA, Unity 3D has been specifically designed for game development, so it comes with multiple game-specific features.
With Unity 3D, you can create both two- and three-dimensional games. It has an all-in-one editor that features storytelling rather than coding, advanced performance profiling tools, a real-time rendering engine, and many other cool features. Besides games, Unity 3D also allows you to build virtual reality applications. The personal license is available for free for anyone whose revenue or funding doesn’t exceed $100K annually.
8. Firebase
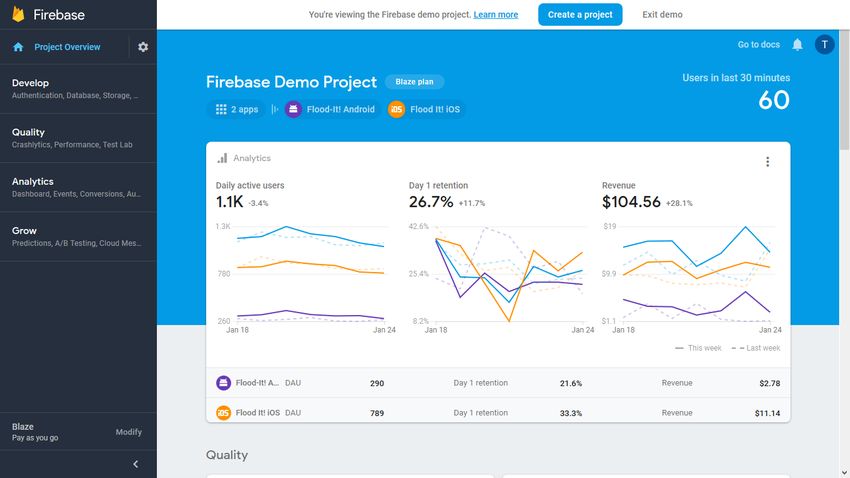
Firebase is a comprehensive mobile and web app development platform by Google. It provides you with tools for managing and monitoring your mobile and web applications. It doesn’t only work with Android but also supports iOS, web, and Unity3D applications. Firebase consists of several individual products that share data and insight with each other. The main Firebase product categories are:
- “Develop”: authentication, database, storage, hosting, etc.
- “Quality”: crash reporting, performance, and testing.
- “Analytics”: conversions, audiences, funnels, etc.
- “Grow”: predictions, A/B testing, cloud and in-app messaging, etc.
The smallest plan called “Spark” is free and includes many Firebase products from performance monitoring to real-time databases, so it’s definitely worth a try.
9. Stetho

Stetho is an open-source debug bridge for Android apps, developed by Facebook. It allows you to connect your app to Google Chrome and debug it using Chrome Developer Tools. After integrating your Android app with Stetho, you can access the debugging UI by navigating to the chrome:inspect URL.
With Stetho, you can use all features of Chrome DevTools’ Network panel to inspect your Android application. You can also visualize your databases and view the app’s hierarchy. Besides, you can enable the additional dumpapp tool that provides you with a command-line interface to further inspect the internals of your application. Dumpapp comes with a couple of default plugins, however, you can create your own dumpapp plugin, too.
10. LeakCanary

LeakCanary is a memory leak detection library for Android and Java, available on GitHub for free. It has been built by the developer team of the Square credit card processing company.
A memory leak is a programming error that frequently occurs in Java and Android applications. It happens when your app keeps a reference to an object that is no longer necessary and should be garbage collected. As the reference still exists, the memory allocated for the expired object cannot be reclaimed. In some cases, memory leaks can lead to OutOfMemoryError crashes, too.
LeakCanary offers an elegant solution to this problem. It identifies objects that are no longer necessary and finds the chain of references that point back to them. Then, it automatically notifies you about the memory leaks and you can use the leak trace to fix the problem.
11. Android Architecture Blueprints
Android Architecture Blueprints is a collection of architectural patterns and tools you can use for Android app development. It’s published by the Google Samples GitHub account maintained by the Google Developers team. Mobile app development is not solely about coding. Before you start programming, you also need to design the architecture of your application.
Android Architecture Blueprints can help you avoid typical architectural mistakes and inconsistencies that might cost you a lot in the long run. For example, here’s the blueprint of a to-do app using the MVP (Model-View-Presenter) architectural pattern.
12. Android Developers
Android Developers is the official source of Android development. You can find loads of Android resources here, completely for free. The materials have been created by Google, so you don’t have to worry about quality. The site is quite comprehensive, so it’s not always easy to find what you’re looking for. Here are some of its most useful resources:
- Android Developer Guides: details how to build Android apps using the Android APIs and other libraries.
- Android Training Courses: offers guided training paths to learn Android development step by step, from beginner to advanced level.
- Android Design Guidelines: provides information about how to design apps that look and behave consistently with the Android platform.
- Google Play Launch Checklist: summarizes the requirements your app has to meet before you submit it to the Google Play store.
Learn More
Android development is rapidly evolving and there’s always something new to learn, even if you are in the industry for many years.
If you are just getting started and need some encouragement, check out our article about what beginners need to know about Android development.
If you have a WordPress site that you want to turn into an Android app, have a look at our collection of mobile app plugins.
And, if you are interested in Java development, too, don’t miss out on our hand-picked selection of the best Java web frameworks.